2025-01-03 Qilu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. HaiPress

JINAN,China,Dec. 25,2024 -- During the 66th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology (ASH) held in San Diego from December 7 to 10,preliminary results from the first human trial of QLS32015,a novel anticancer drug developed by Qilu Pharmaceuticalfor treating relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM),were unveiled(Poster Number: 1990). The findings demonstratedthat QLS32015 showedexcellent anti-tumor activity and was well tolerated by patients withRRMM.
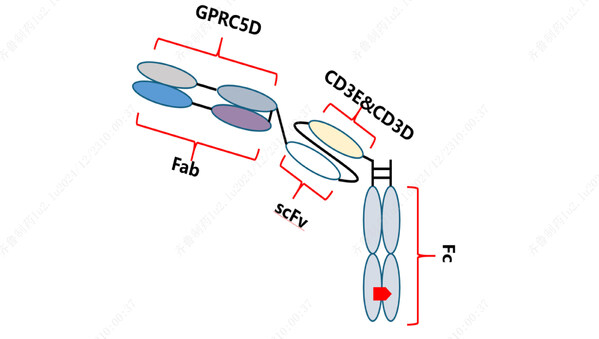
Schematic representation of the structure of QLS32015
QLS32015,a novel humanized IgG1 T-cell retargeting bispecific antibody,targets both GPRC5D,a G protein-coupled receptor class C group 5 member D,and CD3. By bridging CD3-expressing T cells and GPRC5D-expressing tumor cells,QLS32015 facilitates T-cell-mediated destruction of cancer cells. Instead of relying onthe conventional major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and specific T-cell receptor (TCR) binding pathways,this processcreates an immune synapse that activates T cells,triggering them to attack and kill tumor cells. [1-2]
This studyis an open-label,dose-escalation/expansion Phase Iclinical trial (NCT05920876),aimingto assess the safety of QLS32015 in patients with RRMM while offeringpreliminary insights into its efficacy. The studyis led byProf. Lugui Qiu from the Institute of Hematology and Blood Diseases Hospitalatthe Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences.
The study enrolled patients with RRMM who had either progressed on or shown intolerance to existing treatments. These patients received QLS32015 as monotherapy,administered subcutaneously at doses ranging from 2 to 200 μg/kg,either weekly or biweekly. During the Phase Ia dose-escalation phase,the primary endpoints were to identify the dose-limiting toxicities (DLT),the maximum tolerated dose (MTD),and the recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D). The study design employed a combination of accelerated titration and Bayesian optimal interval strategies.
As of August 31,2024,a total of 13 patients had been enrolled in the trial. The median age among these participants was 61 years,and they had undergone a median of 3 prior lines of therapy (range,1 to 8). Notably,76.9% of the patients had received at least triple therapy,which included proteasome inhibitors,immunomodulators,and anti-CD38 monoclonal antibodies. Additionally,23.1% of the participants had been treated with B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy.
In terms of safety,one DLT was observed at the 54 μg/kg dose level,but the MTD was not reached. Treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) were reported in all patients. The most common TRAE was cytokine release syndrome (CRS),occurring at grades 1 or 2 in all patients,with a median duration of 2.1 days. The most common grade ≥3 TRAEs were hematological toxicities,including lymphopenia (92.3%) and thrombocytopenia (61.5%). Most non-hematological TRAEs were grade 1 or 2. Importantly,no cases of immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) were reported,and there were no TRAEs that led to treatment discontinuation or death.
As of the data cut-off,12 out of the 13 enrolled patients had undergone at least one assessment of efficacy. The objective response rate (ORR),assessed according to the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) criteria,was 76.9% (10/13). Among these patients,two (15.4%) achieved complete response (CR),three (23.1%) reached very good partial response (VGPR),and five (38.5%) attained partial response (PR).
The findings suggest that QLS32015 has a tolerable safety profile and shows promising remission rates among RRMM patients. The dose-escalation studyisstill in progress. DLT,MTD,and RP2D are to be determined.
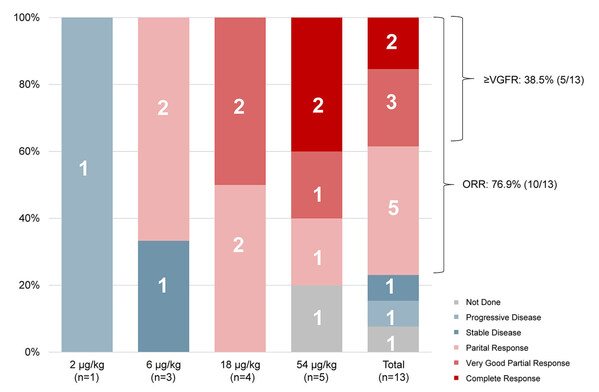
The efficacy of QLS32015 in treating patients with RRMM
References:
1. Li J,et al. 2017;31(3):383-395.
2. Velasquez MP,et al. Blood. 2018;131(1):30-38.
Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other media. The purpose of reprinting is to convey more information. It does not mean that this website agrees with its views and is responsible for its authenticity, and does not bear any legal responsibility. All resources on this site are collected on the Internet. The purpose of sharing is for everyone's learning and reference only. If there is copyright or intellectual property infringement, please leave us a message.
©copyright 2009-2020 Sir Daily Contact Us SiteMap